Introduction
Many AWS customers struggle to balance cloud cost management with employee development. While controlling spending is a priority, empowering teams to experiment is also crucial. Managing sandbox accounts provides a solution: dedicated environments for learning allow organizations to control costs, track usage, and prevent interference with production. Clear policies and tools like AWS Landing Zone Accelerator (LZA) enable innovation while maintaining cost efficiency.
Who and why uses an AWS sandbox account?
AWS sandbox accounts enable users to explore services and test configurations in isolated environments, often for short-term, risk-free experimentation. While distinct from structured, long-term development accounts, sandbox accounts can be used for extended periods. They require management to control costs and security risks, as they offer fewer restrictions for experimentation.
Sandbox Accounts Management Considerations
Sandbox Account Provisioning
The first phase of sandbox account management is provisioning, which involves setting up and configuring the account before assigning it to users or teams. This phase includes:
- Creating the sandbox account
- Provisioning essential resources, such as budget controls, networking, and default business configurations
- Grant access to the account to a user or team
- Updating Metadata – keeping track of the sandbox assignment by updating a dedicated database or using the account tags mechanism (this can be used in Cost Allocation and Cost and Usage reports) is essential.
Since AWS account creation can take time, this factor must be considered when planning the provisioning process.
Sandbox Account Provisioning Methods
There are two main approaches to provisioning sandbox accounts:
1. Pool Accounts
- A predefined number of sandbox accounts are created and kept on hold until needed.
- These accounts remain unused and do not consume resources or incur costs.
- When a sandbox account is needed, it is assigned to a user or team by granting the necessary permissions and provisioning required resources (budget controls, networking, and other configurations).
2. On Demands Accounts
- A sandbox account is created only when needed.
- Asynchronous process, due to the long process of creating accounts.
- Asynchronous to avoid delays.
- Once the account is created, all required resources and permissions are provisioned automatically.
Both approaches help organizations manage sandbox environments efficiently while balancing cost, security, and accessibility.
Sandbox Isolation
Sandbox accounts must be isolated due to their “untrusted zone” nature, where typically restricted actions are allowed. Isolation prevents risks to the organization. This is achieved through:
- Organizational Unit (OU) Isolation: Assigning all sandbox accounts to a specific OU for consistent policy enforcement.
- Network Isolation: Ensuring sandbox networks operate independently to prevent vulnerabilities from accessing internal resources.
Managing Sandbox Account Usage and Costs
Sandbox account usage requires careful control to prevent unnecessary costs from idle or expensive resources. Implement budget controls to monitor spending, alert FinOps teams, and automate actions like restricting access, shutting down resources, or closing the account when limits are exceeded. These controls are vital for preventing cost leaks and ensuring efficient sandbox environment management.
Sandbox Guardrails
Adequate guardrails on sandbox accounts are essential to ensure a secure and isolated environment and prevent unnecessary costs.
This task becomes more manageable with Service Control Policies (SCPs) when using AWS Landing Zone. Among the various SCPs that an organization should enforce, it is recommended to apply the following basic policies:
- Enable CloudTrail on each sandbox account.
- Create and implement VPC flow logs.
- Enable GuardDuty.
- Size limits restrictions to AWS resources.
- Ingress security groups allow up to /24 and/or predefined whitelists and/or permitted other security groups.
- Allow egress traffic to 0.0.0.0 rule.
- Block public S3 bucket.
- Default budget alert.
Sandbox Account Decommissioning
After experimentation, it’s crucial to decommission sandbox accounts due to cost and potential security vulnerabilities. Even for long-term projects, regular cleanup is necessary. The decommissioning process varies depending on the account provisioning method.
Pool Accounts
Decommissioning pool accounts involves terminating the resources associated with the sandbox (using available open-source tools, if applicable) and, if necessary, unassigning the account from the user or team by revoking access and updating the sandbox metadata.
On-Demand Accounts
Decommissioning on-demand accounts involves closing the account using the regular AWS procedure and updating the sandbox metadata accordingly. The number of accounts that can be closed in a period is limited, so this should be considered when using this method.
ITSM Integration – optional
Integrating an IT Service Management (ITSM) system with an integration platform is crucial for smooth communication between systems in today’s digital environment. This integration bridges local and cloud-based solutions, simplifies workflows, automates processes, and offers users a familiar interface.
Sandbox Account in AWS Landing Zone
Secure and govern sandbox accounts using AWS Landing Zone, a pre-configured, multi-account environment that simplifies setup and enforces best practices. This approach reduces misconfigurations and streamlines security. Utilize AWS Landing Zone capabilities for effective sandbox management.
-
- Sandbox Organizational Unit (OU) – Employing a dedicated Sandbox Organizational Unit (OU) facilitates the application of organizational best practices, security measures, and cost management. By implementing policies at the OU level, all sandbox accounts adhere to standardized controls, ensuring consistent security, governance, and cost optimization across all environments.
2. Service Control Policies (SCPs) – You can use SCP to secure and control the costs of sandbox accounts by:
a. Restrict High-Cost Services
b. Set regional restrictions
c. Enforce budget actions
d.Deny the use of risky services
3. Control Tower’s Account Factory – The Account Factory is a configurable account template that standardizes the provisioning of new accounts with pre-approved configurations, ensuring consistency and compliance across your organization. It can also be leveraged to provision sandbox accounts.
- Sandbox Organizational Unit (OU) – Employing a dedicated Sandbox Organizational Unit (OU) facilitates the application of organizational best practices, security measures, and cost management. By implementing policies at the OU level, all sandbox accounts adhere to standardized controls, ensuring consistent security, governance, and cost optimization across all environments.
AllCloud’s Sandbox Management Add-On for AWS Landing Zone Accelerator (LZA)
To enhance sandbox account management, AllCloud has developed a solution that integrates key sandbox management concepts and builds on AWS LZA capabilities.
The LZA features that will be used when implementing the solution are:
- Create a dedicated organizational unit for Sandboxes.
- Apply predefined (comes with the solution) guardrails on the Sandboxes OU.
- Utilize LZA VPC templates to deploy a basic networking configuration for the Sandbox account.
- Create a Pool of Sandbox accounts.
- Use LZA customs to accomplish any customer special requirements – optional
- Create a delegated admin sandbox management account to provision AllCloud’s solution
The solution is deployed on a delegated admin account. It allows the organization to manage sandbox accounts and track sandbox usage using a dedicated database.
Sandbox Account Allocation
A central EventBridge event bus manages sandbox account requests from integrations like AWS Service Catalog or Jira. These integrations send allocation requests, triggering the process, while subscribing to status change events for real-time tracking.
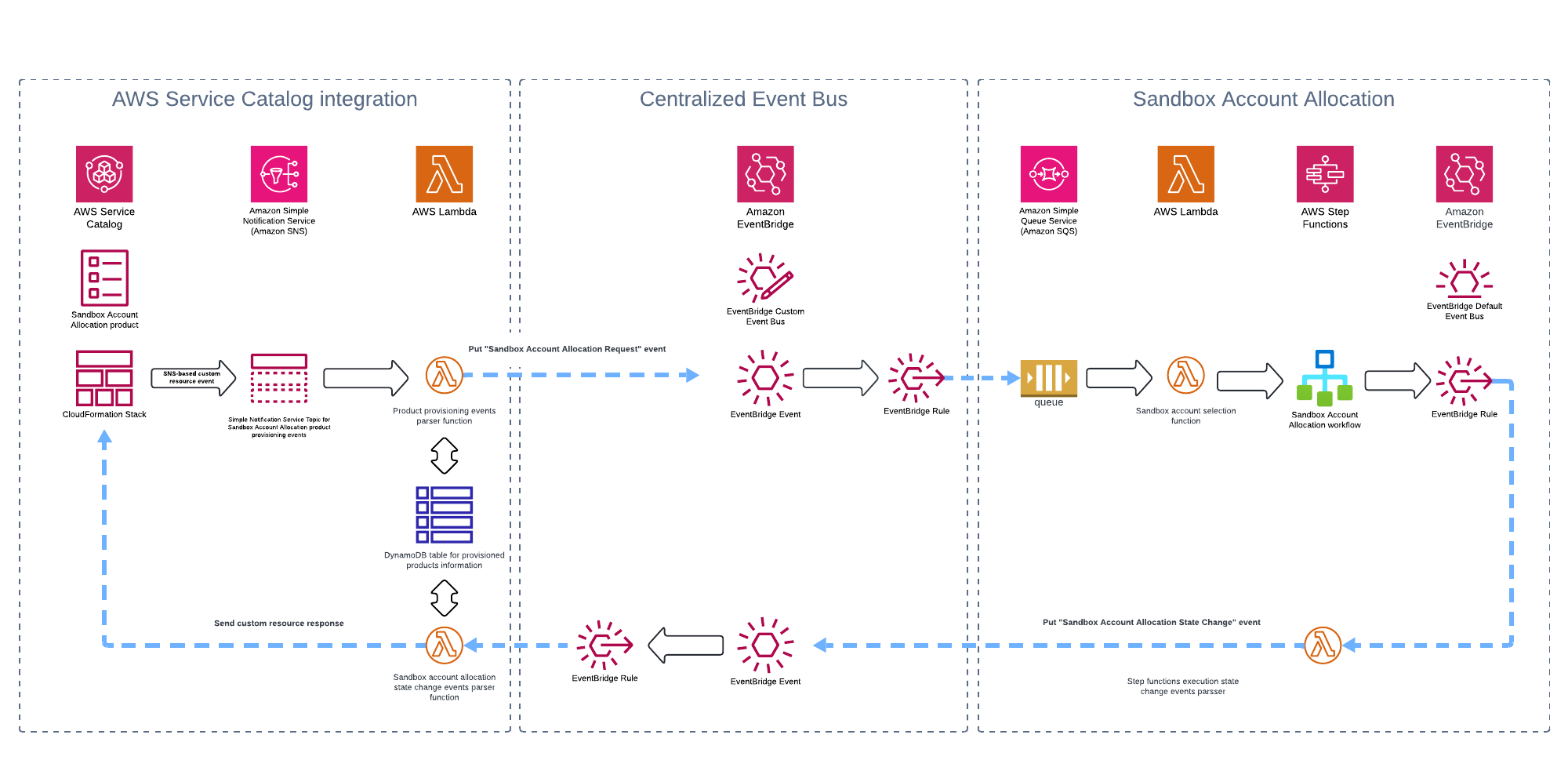
AWS Service Catalog integration
The solution contains out-of-the-box integration with the AWS service catalog as a front-end to manage the sandbox accounts. However, using the centralized event bus, you can also integrate the solution with the organization’s ITSM.
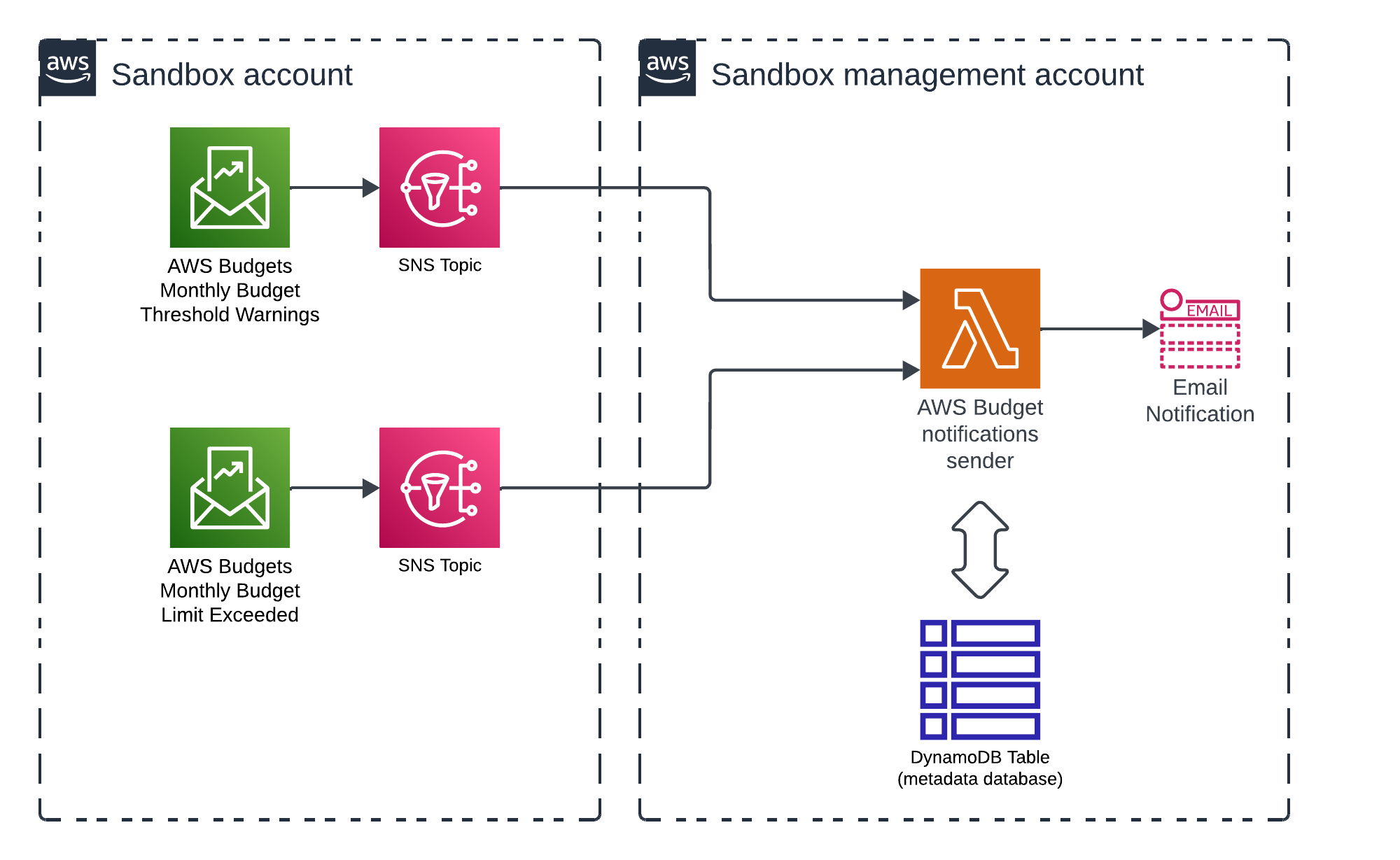
Budget notifications
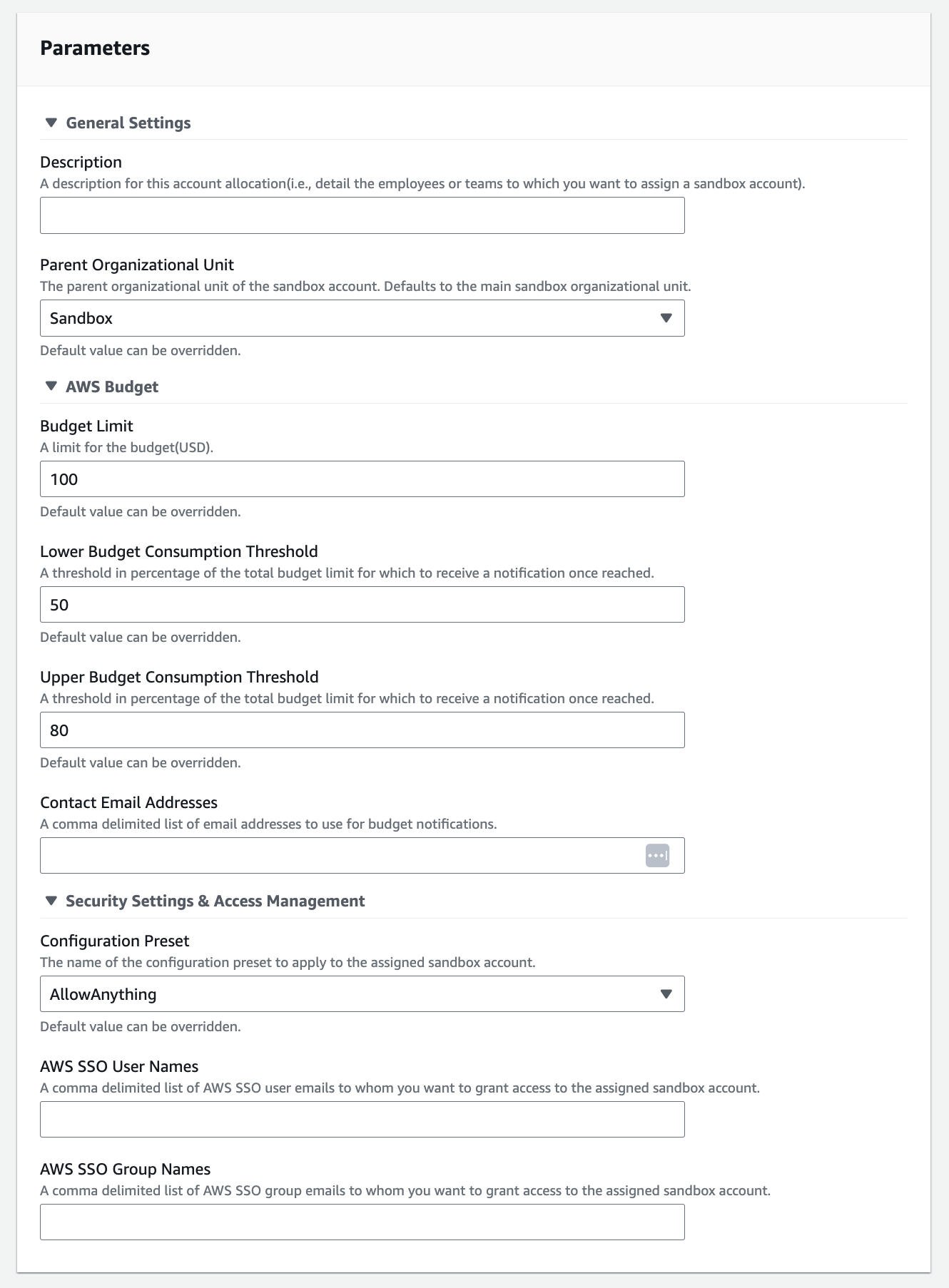
The budget notifications component emails budget notifications to sandbox account owners. The solution creates two SNS topics in every sandbox account. These topics receive notifications from AWS Budget when predefined thresholds are exceeded(e.g., at 50 and 80 percent of the total budget limit) and when the budget limit is met.
Summary
AWS Sandbox accounts enable isolated testing environments. Effective management includes proper provisioning, isolation, cost controls, and decommissioning. Security is maintained via Service Control Policies and guardrails like CloudTrail and GuardDuty. AWS Landing Zone integration offers pre-configured security and automated governance. This approach balances innovation with security and cost efficiency.

Avihu Cohen
Solutions Architect